Abstract
Background
In pediatric hematologic malignancy, the incidence of invasive fungal infections (IFI) is ~ 5-10% and leads to significant morbidity and mortality. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) accounts for the largest group at risk and has the largest absolute number of IFI. Antifungal prophylaxis has the potential to mitigate risk of invasive infections in ALL but is not currently standard of care due to the paucity of data in ALL subgroups. A recent systematic review showed a significant reduction in proven/probable IFI and fungal infection-related mortality in pediatric patients when using a mold active agent compared with fluconazole, therefore an echinocandin was selected for systemic antifungal prophylaxis in our institution. In this study we investigate the incidence of IFI in patients with ALL in a highly endemic area (Ohio River Valley) and describe the impact of echinocandin prophylaxis in this population.
Methods
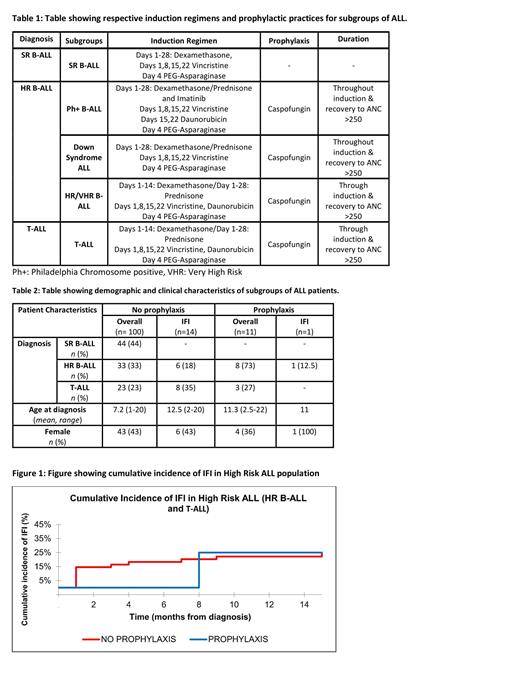
We conducted a retrospective cohort study of consecutive patients <25 years with ALL from 2015 to 2021 at Norton Children's Hospital, Louisville, KY. IFI was classified as possible, probable, or proven as defined by the 2020 European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer/ Mycoses Study Group Consensus Group. Patients were then analyzed in 2 subgroups based on prophylaxis with caspofungin. Inpatient administration of caspofungin was given to patients with high-risk B-ALL (HR B-ALL) and T-ALL as outlined in Table 1. Patient and IFI characteristics were collected, and cumulative incidence analyses used for subgroup comparisons.
Results
Demographics and patient characteristics are summarized in Table 2. Between 2015 to 2020 we identified 100 patients with ALL. Mean age at diagnosis was 7.2 years and 43% were female. We identified 14 unique cases of IFI in 13 patients with ALL who did not receive prophylaxis with caspofungin during 2015 to 2020 (14%). Prior to the implementation of prophylaxis, IFI occurred in 0% (0/43) of the SR B-ALL group, 18.2% (6/33) in HR B-ALL group and 35% (8/23) in T-ALL group. IFI incidence was highest in induction and consolidation phases (71.4%) and implicated species during these phases included Aspergillus, Candida, Fusarium, and Papulasopora. From April 2020 to July 2021, there were 22 newly diagnosed patients with ALL, 11 (50%) of whom received inpatient prophylaxis with caspofungin. There was 1 case (4.5%) of reported IFI during delayed intensification (no prophylaxis at the time of infection). As seen in Figure 1, patients with HR B-ALL and T-ALL who were hospitalized and received caspofungin during induction saw a notable decrease in the cumulative incidence of IFI, from 18.3% to 0% at 6 months into treatment before reaching similar levels in the patients who did not receive prophylaxis.
Conclusion
In our pediatric population, patients with T-ALL and HR B-ALL were more likely to develop IFI than those with SR B-ALL. Prophylaxis with caspofungin and inpatient hospitalization during induction were effective strategies for reducing the incidence of IFI in induction and consolidation for our high-risk leukemia population. This approach should be validated in larger studies with special consideration being given to patients in fungal endemic areas.
Raj: Terumo Medical Corporation: Honoraria, Speakers Bureau; Forma therapeutics: Consultancy; Global biotherapeutics: Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
 This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal